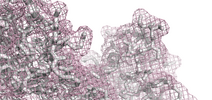
SB0076 : p35, cyclin-dependent kinase 5, regulatory subunit 1
[ CaMP Format ]
* Basic Information
| Organism | Homo sapiens (human) |
| Protein Names | cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activator 1 [Homo sapiens]; cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activator 1; TPKII regulatory subunit; regulatory partner for CDK5 kinase; CDK5 activator 1; tau protein kinase II 23kDa subunit; neuronal CDK5 activator; cyclin-dependent kinase 5 regulatory subunit 1; Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activator 1; Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 regulatory subunit 1; Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activator 1, p35; p35; Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activator 1, p25; p25; Tau protein kinase II 23 kDa subunit; p23 |
| Gene Names | CDK5R1; CDK5R, NCK5A; CDK5R; NCK5A; cyclin-dependent kinase 5, regulatory subunit 1 (p35) |
| Gene Locus | 17q11.2; chromosome 17 |
| GO Function | Not available |
* Information From OMIM
Function: CDK5 is required for proper development of the mammalian central nervous system. To be activated, CDK5 must associate with its regulatory subunit, p35. Patrick et al. (1999) showed that p25, a truncated form of p35, accumulates in neurons in the brains of patients with Alzheimer disease (OMIM:104300). This accumulation correlated with an increase in CDK5 kinase activity. Unlike p35, p25 was not readily degraded, and binding of p25 to CDK5 constitutively activated CDK5, changed its cellular location, and altered its substrate specificity. In vivo, the p25/CDK5 complex hyperphosphorylated tau (OMIM:157140), which reduced tau's ability to associate with microtubules. Moreover, expression of the p25/CDK5 complex in cultured primary neurons induced cytoskeletal disruption, morphologic degeneration, and apoptosis. Patrick et al. (1999) concluded that cleavage of p35, followed by accumulation of p25, may be involved in the pathogenesis of cytoskeletal abnormalities and neuronal death in neurodegenerative diseases.
* Structure Information
1. Primary Information
Length: 307 aa
Average Mass: 34.060 kDa
Monoisotopic Mass: 34.039 kDa
2. Domain Information
Annotated Domains: interpro / pfam / smart / prosite
Computationally Assigned Domains (Pfam+HMMER):
| domain name | begin | end | score | e-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
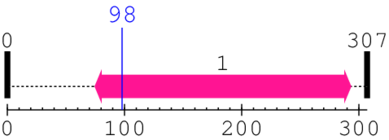
| Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activator protein 1. | 75 | 293 | 135.0 | 1.7 |
| --- cleavage 98 (inside Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activator protein 75..293) --- | ||||
3. Sequence Information
Fasta Sequence: SB0076.fasta
Amino Acid Sequence and Secondary Structures (PsiPred):
* Cleavage Information
1 [sites] cleaved by Calpain 2
Source Reference: [PubMed ID: 10830966] Lee MS, Kwon YT, Li M, Peng J, Friedlander RM, Tsai LH, Neurotoxicity induces cleavage of p35 to p25 by calpain. Nature. 2000 May 18;405(6784):360-4.
Cleavage sites (±10aa)
[Site 1] SLSCANLSTF98-AQPPPAQPPA
Phe98  Ala
Ala
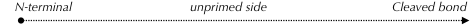 |
|||||||||
| P10 | P9 | P8 | P7 | P6 | P5 | P4 | P3 | P2 | P1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ser89 | Leu90 | Ser91 | Cys92 | Ala93 | Asn94 | Leu95 | Ser96 | Thr97 | Phe98 |
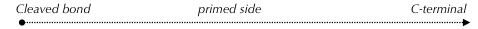 |
|||||||||
| P1' | P2' | P3' | P4' | P5' | P6' | P7' | P8' | P9' | P10' |
| Ala99 | Gln100 | Pro101 | Pro102 | Pro103 | Ala104 | Gln105 | Pro106 | Pro107 | Ala108 |
 Sequence conservation (by blast)
Sequence conservation (by blast)
* References
[PubMed ID: 24085300] Saito T, Yano M, Kawai Y, Asada A, Wada M, Doi H, Hisanaga S, Structural basis for the different stability and activity between the Cdk5 complexes with p35 and p39 activators. J Biol Chem. 2013 Nov 8;288(45):32433-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.512293. Epub 2013