SB0110 : Caspase-7
[ CaMP Format ]
* Basic Information
| Organism | Homo sapiens (human) |
| Protein Names | caspase-7 isoform alpha precursor [Homo sapiens]; caspase-7 isoform alpha precursor; caspase 7, apoptosis-related cysteine protease; ICE-like apoptotic protease 3; apoptotic protease MCH-3; Caspase-7; CASP-7; 3.4.22.60; Apoptotic protease Mch-3; CMH-1; ICE-LAP3; Caspase-7 subunit p20; Caspase-7 subunit p11 |
| Gene Names | CASP7; MCH3; caspase 7, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase |
| Gene Locus | 10q25; chromosome 10 |
| GO Function | Not available |
* Information From OMIM
Description: Programmed cell death (apoptosis) is associated with the hierarchical activation of a number of cysteine proteinases with cleavage preference after asparagine residues, comprising the caspase family C14 of clan CD (Barrett and Rawlings, 2001). Based on their position within this proteolytic cascade, caspases are subdivided into initiator caspases, which include caspase-8 (OMIM:601763) and caspase-9 (OMIM:602234), and executioner caspases, which include caspase-3 (OMIM:600636, also called CPP32), caspase-6 (OMIM:601532, also called MCH2), and caspase-7, as well as a third group of caspases involved in cytokine activation, namely, caspase-1 (OMIM:147678, also called ICE), caspase-4 (OMIM:602664), and caspase-5 (OMIM:602665). In apoptosis, the upstream caspases triggered by cofactor-mediated transactivation activate the downstream executioner caspases by limited proteolysis. These executioners, in turn, cleave distinct intracellular proteins involved in promoting the apoptotic phenotype.
* Structure Information
1. Primary Information
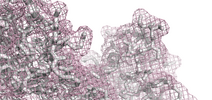
Length: 303 aa
Average Mass: 34.276 kDa
Monoisotopic Mass: 34.255 kDa
2. Domain Information
Annotated Domains: interpro / pfam / smart / prosite
Computationally Assigned Domains (Pfam+HMMER):
| domain name | begin | end | score | e-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| --- cleavage 36 --- | ||||
| Caspase domain 1. | 68 | 301 | 1.0 | 0.0 |
3. Sequence Information
Fasta Sequence: SB0110.fasta
Amino Acid Sequence and Secondary Structures (PsiPred):
4. 3D Information
Known Structures in PDB: 1F1J (X-ray; 235 A; A/B=2-303), 1GQF (X-ray; 290 A; A/B=47-303), 1I4O (X-ray; 240 A; A/B=24-303), 1I51 (X-ray; 245 A; A/C=51-198, B/D=199-303), 1K86 (X-ray; 260 A; A/B=51-303), 1K88 (X-ray; 270 A; A/B=51-303), 1KMC (X-ray; 290 A; A/B=1-303), 1MIA (Model; -; A=57-193, B=211-303), 1SHJ (X-ray; 280 A; A/B=50-303), 1SHL (X-ray; 300 A; A/B=57-303), 2QL5 (X-ray; 234 A; A/C=24-196, B/D=207-303), 2QL7 (X-ray; 240 A; A/C=24-196, B/D=207-303), 2QL9 (X-ray; 214 A; A/C=24-196, B/D=207-303), 2QLB (X-ray; 225 A; A/C=24-196, B/D=207-303), 2QLF (X-ray; 280 A; A/C=24-196, B/D=207-303), 2QLJ (X-ray; 260 A; A/C=24-196, B/D=207-303), 3EDR (X-ray; 245 A; A/C=24-196, B/D=207-303), 3H1P (X-ray; 261 A; A/B=50-303), 3IBC (X-ray; 275 A; A/C=24-196, B/D=207-303), 3IBF (X-ray; 250 A; A/C=24-196, B/D=207-303), 3R5K (X-ray; 286 A; A/B=1-303), 4FDL (X-ray; 280 A; A/B=2-303), 4FEA (X-ray; 379 A; A/B=57-303), 4HQ0 (X-ray; 300 A; A/B=47-303), 4HQR (X-ray; 300 A; A/B=47-303), 4JB8 (X-ray; 170 A; A=24-198, B=207-303), 4JJ8 (X-ray; 294 A; A/B=57-303), 4JR1 (X-ray; 215 A; A/B=57-303), 4JR2 (X-ray; 165 A; A/B=57-303), 4LSZ (X-ray; 226 A; A/C=24-198, B/D=207-303)
* Cleavage Information
1 [sites] cleaved by Calpain 1
Source Reference: [PubMed ID: 19617626] Gafni J, Cong X, Chen SF, Gibson BW, Ellerby LM, Calpain-1 cleaves and activates caspase-7. J Biol Chem. 2009 Sep 11;284(37):25441-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.038174. Epub 2009
Cleavage sites (±10aa)
[Site 1] DRSSFVPSLF36-SKKKKNVTMR
Phe36 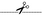 Ser
Ser
 |
|||||||||
| P10 | P9 | P8 | P7 | P6 | P5 | P4 | P3 | P2 | P1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asp27 | Arg28 | Ser29 | Ser30 | Phe31 | Val32 | Pro33 | Ser34 | Leu35 | Phe36 |
 |
|||||||||
| P1' | P2' | P3' | P4' | P5' | P6' | P7' | P8' | P9' | P10' |
| Ser37 | Lys38 | Lys39 | Lys40 | Lys41 | Asn42 | Val43 | Thr44 | Met45 | Arg46 |
 Sequence conservation (by blast)
Sequence conservation (by blast)
* References
[PubMed ID: 24434142] Wakao K, Watanabe T, Takadama T, Ui S, Shigemi Z, Kagawa H, Higashi C, Ohga R, Taira T, Fujimuro M, Sangivamycin induces apoptosis by suppressing Erk signaling in primary effusion lymphoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Feb 7;444(2):135-40. doi: