XSB0121 : caspase 9 isoform beta preproprotein [Homo sapiens]
[ CaMP Format ]
This entry is computationally expanded from SB0042
* Basic Information
| Organism | Homo sapiens (human) |
| Protein Names | Caspase-9; CASP-9; 3.4.22.62; ICE-like apoptotic protease 6; ICE-LAP6; Apoptotic protease Mch-6; Apoptotic protease-activating factor 3; APAF-3; Caspase-9 subunit p35; Caspase-9 subunit p10; caspase 9 isoform beta preproprotein; caspase 9; apoptosis-related cysteine protease; apoptotic protease activating factor 3 |
| Gene Names | CASP9; MCH6; caspase 9, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase |
| Gene Locus | 1p36.3-p36.1; chromosome 1 |
| GO Function | Not available |
* Information From OMIM
Function: Li et al. (1997) determined that caspase-9 and APAF1 (OMIM:602233) bind to each other via their respective NH2-terminal CED-3 homologous domains in the presence of cytochrome c (OMIM:123970) and dATP, an event that leads to caspase-9 activation. Activated caspase-9 in turn cleaves and activates caspase-3. Depletion of caspase-9 from S-100 extracts diminished caspase-3 activation. Mutation of the active site of caspase-9 (cys287 to ala) attenuated the activation of caspase-3 and cellular apoptotic response in vivo, indicating that caspase-9 is the most upstream member of the apoptotic protease cascade that is triggered by cytochrome c and dATP.
Function: Activation of procaspase-9 by APAF1 in the cytochrome c/dATP-dependent pathway requires proteolytic cleavage to generate the mature caspase molecule. Srinivasula et al. (1998) showed that deletion of the APAF1 WD40 repeats makes APAF1 constitutively active and capable of processing procaspase-9 independent of cytochrome c and dATP. APAF1-mediated processing of procaspase-9 occurs at asp315 by an intrinsic autocatalytic activity of procaspase-9 itself. Srinivasula et al. (1998) provided evidence that APAF1 can form oligomers and may facilitate procaspase-9 autoactivation by oligomerizing its precursor molecules. Once activated, caspase-9 can initiate a biochemical cascade involving the downstream executioners caspase-3, -6, and -7.
Function: XIAP (OMIM:300079) interacts with caspase-9 and inhibits its activity, whereas SMAC (OMIM:605219) relieves this inhibition through interaction with XIAP. Srinivasula et al. (2001) demonstrated that XIAP associates with the active caspase-9-APAF1 holoenzyme complex through binding to the amino terminus of the linker peptide on the small subunit of caspase-9, which becomes exposed after proteolytic processing of procaspase-9 at asp315. Supporting this observation, point mutations that abrogate the proteolytic processing but not the catalytic activity of caspase-9, or deletion of the linker peptide, prevented caspase-9 association with XIAP and its concomitant inhibition. Srinivasula et al. (2001) noted that the N-terminal 4 residues of caspase-9 linker peptide share significant homology with the N-terminal tetrapeptide in mature SMAC and in the Drosophila proteins Hid/Grim/Reaper, defining a conserved class of IAP-binding motifs. Consistent with this finding, binding of the caspase-9 linker peptide and SMAC to the BIR3 domain of XIAP is mutually exclusive, suggesting that SMAC potentiates caspase-9 activity by disrupting the interaction of the linker peptide of caspase-9 with BIR3. Srinivasula et al. (2001) concluded that their studies reveal a mechanism in which binding to the BIR3 domain of XIAP by 2 conserved peptides, one from SMAC and the other from caspase-9, has opposing effects on caspase activity and apoptosis.
Function: Marsden et al. (2002) established that the cell death pathway controlled by BCL2 (OMIM:151430) does not require caspase-9 or its activator APAF1. In keeping with their evidence that neither is required for hematopoietic homeostasis, in which the BCL2 family has major roles, deletion of thymocytes with self-reactivity depends on BIM (OMIM:603827) but not on APAF1. Because apoptosis was at most slightly delayed by the absence of APAF1 or caspase-9, Marsden et al. (2002) concluded that the apoptosome is not an essential trigger for apoptosis but is rather a machine for amplifying the caspase cascade. They found that BCL2 overexpression increased lymphocyte numbers in mice and inhibited many apoptotic stimuli, but the absence of APAF1 and caspase-9 did not. Caspase activity was still discernible in cells lacking APAF1 or caspase-9 and a potent caspase antagonist both inhibited apoptosis and retarded cytochrome c release. Marsden et al. (2002) concluded that BCL2 regulates a caspase activation program independently of the cytochrome c/APAF1/caspase-9 apoptosome, which seems to amplify rather than initiate the caspase cascade.
Function: CASP9 activity increases dramatically upon association with the apoptosome complex. Yin et al. (2006) and Pop et al. (2006) demonstrated that the apoptosome activates CASP9 by causing its dimerization due to induced proximity. In addition, Yin et al. (2006) found that the apoptosome enhanced the affinity of CASP9 for proCASP3, either by directly interacting with proCASP3 or by inducing a conformational change in bound CASP9.
* Structure Information
1. Primary Information
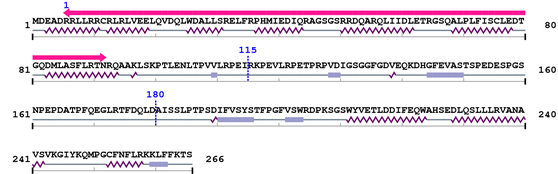
Length: 266 aa
Average Mass: 30.184 kDa
Monoisotopic Mass: 30.165 kDa
2. Domain Information
Annotated Domains: interpro / pfam / smart / prosite
Computationally Assigned Domains (Pfam+HMMER):
| domain name | begin | end | score | e-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CARD 1. | 6 | 92 | 91.5 | 3e-24 |
3. Sequence Information
Fasta Sequence: XSB0121.fasta
Amino Acid Sequence and Secondary Structures (PsiPred):
* Cleavage Information
2 [sites]
Cleavage sites (±10aa)
[Site 1] EGLRTFDQLD180-AISSLPTPSD
Asp180  Ala
Ala
 |
|||||||||
| P10 | P9 | P8 | P7 | P6 | P5 | P4 | P3 | P2 | P1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glu171 | Gly172 | Leu173 | Arg174 | Thr175 | Phe176 | Asp177 | Gln178 | Leu179 | Asp180 |
 |
|||||||||
| P1' | P2' | P3' | P4' | P5' | P6' | P7' | P8' | P9' | P10' |
| Ala181 | Ile182 | Ser183 | Ser184 | Leu185 | Pro186 | Thr187 | Pro188 | Ser189 | Asp190 |
 Sequence conservation (by blast)
Sequence conservation (by blast) Sequence conservation (by blast)
Sequence conservation (by blast)
| Reference peptide (cleaved bond±30 residues) |
|---|
| TSPEDESPGSNPEPDATPFQEGLRTFDQLDAISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG |
Summary
| # | organism | max score | hits | top seq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | N/A | 129.00 | 29 | B |
| 2 | Homo sapiens | 129.00 | 13 | caspase-9 |
| 3 | Pan troglodytes | 129.00 | 6 | PREDICTED: caspase 9 isoform 2 |
| 4 | synthetic construct | 129.00 | 6 | Homo sapiens caspase 9, apoptosis-related cysteine |
| 5 | Macaca mulatta | 117.00 | 6 | PREDICTED: similar to caspase 9 isoform alpha prep |
| 6 | Macaca fascicularis | 117.00 | 2 | caspase 9 |
| 7 | Felis catus | 107.00 | 3 | CASP9 |
| 8 | Canis familiaris | 105.00 | 3 | PREDICTED: caspase 9, apoptosis-related cysteine p |
| 9 | Canis lupus familiaris | 105.00 | 2 | caspase 9 |
| 10 | Monodelphis domestica | 97.40 | 3 | PREDICTED: similar to ICE-LAP6 |
| 11 | Rattus norvegicus | 96.30 | 5 | caspase 9 |
| 12 | Mus musculus | 91.30 | 12 | unnamed protein product |
| 13 | Gallus gallus | 73.90 | 2 | caspase 9 |
| 14 | Dicentrarchus labrax | 69.70 | 2 | caspase-9 |
| 15 | Xenopus laevis | 66.20 | 6 | caspase-9 |
| 16 | Danio rerio | 65.90 | 4 | Zgc:101776 protein |
| 17 | Tetraodon nigroviridis | 65.10 | 2 | unnamed protein product |
| 18 | Oncorhynchus mykiss | 60.80 | 1 | caspase-9 |
| 19 | Oryctolagus cuniculus | 52.00 | 3 | caspase 9 |
| 20 | Tribolium castaneum | 40.40 | 1 | PREDICTED: similar to Caspase precursor (drICE), p |
| 21 | Branchiostoma floridae | 40.00 | 1 | AF412335_1 amphiCASP-3/7 |
| 22 | Schistosoma japonicum | 39.30 | 4 | SJCHGC04214 protein |
| 23 | Anopheles gambiae str. PEST | 38.50 | 10 | ENSANGP00000008707 |
| 24 | Aedes aegypti | 38.10 | 2 | caspase-1 |
| 25 | Strongylocentrotus purpuratus | 37.70 | 4 | PREDICTED: similar to caspase-3, partial |
| 26 | Xenopus tropicalis | 37.70 | 2 | caspase 7, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase |
| 27 | Contains: Caspase-3 p17 subunit; Caspase-3 p12 subunit | 36.60 | 3 | CASP3_CRILO Caspase-3 precursor (CASP-3) (Apopain) |
| 28 | Bos taurus | 35.80 | 4 | PREDICTED: similar to Mch3 isoform alpha |
| 29 | Geodia cydonium | 35.80 | 2 | caspase 3 |
| 30 | Equus caballus | 35.40 | 3 | caspase-3 |
| 31 | Gobius niger | 35.00 | 1 | caspase 3 |
| 32 | Sus scrofa | 34.70 | 1 | caspase 3 |
| 33 | Cricetulus griseus | 34.30 | 1 | caspase 3 |
| 34 | Contains: Caspase-7 subunit p20; Caspase-7 subunit p11 | 34.30 | 1 | CASP7_MESAU Caspase-7 precursor (CASP-7) (ICE-like |
| 35 | Salmo salar | 33.90 | 2 | caspase 7 |
| 36 | Ovis aries | 33.90 | 1 | caspase-3 |
| 37 | Drosophila melanogaster | 33.50 | 3 | drICE protein |
| 38 | Drosophila pseudoobscura | 33.50 | 2 | GA20588-PA |
| 39 | Apis mellifera | 33.50 | 1 | PREDICTED: similar to Caspase precursor (drICE) |
| 40 | Chrysiptera parasema | 33.10 | 1 | caspase 3 |
| 41 | Oryzias latipes | 33.10 | 1 | caspase 3A |
| 42 | Aspergillus clavatus NRRL 1 | 32.70 | 1 | pentatricopeptide repeat protein |
| 43 | Takifugu rubripes | 32.30 | 2 | caspase 3 |
Top-ranked sequences
| organism | matching |
|---|---|
| N/A | Query 151 TSPEDESPGSNPEPDATPFQEGLRTFDQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||#|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||| Query 151 TSPEDESPGSNPEPDATPFQEGLRTFDQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 |
| Homo sapiens | Query 151 TSPEDESPGSNPEPDATPFQEGLRTFDQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||#|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||| Query 151 TSPEDESPGSNPEPDATPFQEGLRTFDQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 |
| Pan troglodytes | Query 151 TSPEDESPGSNPEPDATPFQEGLRTFDQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||#|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||| Query 151 TSPEDESPGSNPEPDATPFQEGLRTFDQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 |
| synthetic construct | Query 151 TSPEDESPGSNPEPDATPFQEGLRTFDQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||#|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||| Query 151 TSPEDESPGSNPEPDATPFQEGLRTFDQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 |
| Macaca mulatta | Query 151 TSPEDESPGSNPEPDATPFQEGLRTFDQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 ||||||| ||||||||||||| ||||||||#|+||||||||||||||||||||| |||||| Sbjct 301 TSPEDESSGSNPEPDATPFQEDLRTFDQLD#AVSSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSLRDPKSG 360 |
| Macaca fascicularis | Query 151 TSPEDESPGSNPEPDATPFQEGLRTFDQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 ||||||| ||||||||||||| ||||||||#|+||||||||||||||||||||| |||||| Sbjct 287 TSPEDESSGSNPEPDATPFQEDLRTFDQLD#AVSSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSLRDPKSG 346 |
| Felis catus | Query 151 TSPEDESPGSNPEPDATPFQEGLRTFDQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 ||||| +|||+||||| |||| |||| |#|+|||||||||||||||||||||||| ||| Sbjct 254 TSPEDRTPGSDPEPDAVAFQEGPGTFDQPD#AVSSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDTKSG 313 |
| Canis familiaris | Query 152 SPEDESPGSNPEPDATPFQEGLRTFDQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 |||| ||||+ |||| ||||| |||||#|+|||||||||||||||||||||||+ ||| Sbjct 301 SPEDRSPGSDSEPDAVPFQEGPGPFDQLD#AVSSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRNTKSG 359 |
| Canis lupus familiaris | Query 152 SPEDESPGSNPEPDATPFQEGLRTFDQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 |||| ||||+ |||| ||||| |||||#|+|||||||||||||||||||||||+ ||| Sbjct 332 SPEDRSPGSDSEPDAVPFQEGPGPFDQLD#AVSSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRNTKSG 390 |
| Monodelphis domestica | Query 153 PEDESPGSNPEPDATPFQEGLRTFDQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 |||+||||+|| |||||| ||| |#|++|||||||| |||||||||||||||||| Sbjct 298 PEDKSPGSDPETDATPFQNN---FDQPD#AVASLPTPSDILVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 352 |
| Rattus norvegicus | Query 151 TSPEDESPGSNPEPDATPFQEGLRTFDQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 || +|++ |+ |||| |+||| || ||||#|+||||||||| |||||||||||||| ||| Sbjct 339 TSSQDKAFDSDSEPDAVPYQEGPRTLDQLD#AVSSLPTPSDILVSYSTFPGFVSWRDKKSG 398 |
| Mus musculus | Query 151 TSPEDESPGSNPEPDATPFQEGLRTFDQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 || + + |+ |||| |+||| | ||||#|+||||||||| |||||||||||||| ||| Sbjct 338 TSSQGRTLDSDSEPDAVPYQEGPRPLDQLD#AVSSLPTPSDILVSYSTFPGFVSWRDKKSG 397 |
| Gallus gallus | Query 152 SPEDESPGSNPEPDATPFQEGLRTFDQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 ||+||+ + | || ||| |+ |#|++||||| || |||||||||||||| || Sbjct 289 SPQDETCRRSIESDAIPFQAPSGNEDEPD#AVASLPTPGDILVSYSTFPGFVSWRDKVSG 347 |
| Dicentrarchus labrax | Query 152 SPEDESP---GSNPEPDATPFQ---EGLRTFDQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWR 205 ||++ | |++ + || | + | | |+||#| +|||||||| ||||||||+|||| Sbjct 309 SPDEVEPSIGGADDQTDAIPTSSSSDSLSTSDELD#ARASLPTPSDILVSYSTFPGYVSWR 368 Query 206 DPKSG 210 | +|| Sbjct 369 DTQSG 373 |
| Xenopus laevis | Query 156 ESPGSNP-----EPDATPFQEGLRTFDQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 |+| +| + |||| | |++|#|+|++|||||| ||||||||+||||| +| Sbjct 284 ETPPLSPTSTSLQSDATPVFSGEGDRDEVD#AVSNIPTPSDILVSYSTFPGYVSWRDKHTG 343 |
| Danio rerio | Query 152 SPEDESP---GSNPEPDATPFQEGLRTF----DQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSW 204 ||+| | | + | || | + |+||#| +|||||||| ||||||||+||| Sbjct 310 SPDDVQPCIGGIDDEMDAIPMSSSSDSLSTASDELD#ARASLPTPSDILVSYSTFPGYVSW 369 Query 205 RDPKSG 210 || ++| Sbjct 370 RDTEAG 375 |
| Tetraodon nigroviridis | Query 152 SPEDESP---GSNPEPDATPFQ---EGLRTFDQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWR 205 ||++ | |++ + || | + | |+ |#| +|||| ||| ||||||||+|||| Sbjct 295 SPDEFEPPVVGADDQTDAIPVSSSSDSLSMSDEPD#ARASLPTSSDILVSYSTFPGYVSWR 354 Query 206 DPKSG 210 |||+| Sbjct 355 DPKAG 359 |
| Oncorhynchus mykiss | Query 152 SPEDESP---GSNPEPDATPFQEGLRTF----DQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSW 204 +|+++ | |++ + || | + |+ |#| ++||||||| ||||||||+||| Sbjct 309 TPDEDRPCIGGTDDQTDAMPMSSSSDSLSTPSDEPD#ARATLPTPSDILVSYSTFPGYVSW 368 Query 205 RDPKSG 210 || ++| Sbjct 369 RDTQAG 374 |
| Oryctolagus cuniculus | Query 151 TSPEDESPGSNPEPDATPFQEGLRTFDQLD#AISSLPTPSDI 191 || + + |+ |||| | ||| | +|||#|+||||||||| Sbjct 175 TSSQGRTLDSDSEPDAVPHQEGPRPLNQLD#AVSSLPTPSDI 215 |
| Tribolium castaneum | Query 180 D#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 |# ++| +|| | ||| || ||||||+| Sbjct 81 D#VSYTIPIMADILVMYSTVEGFYSWRDPKNG 111 |
| Branchiostoma floridae | Query 164 PDATPFQEGLRTFDQLD#A--ISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 ||| | + |+||#| ++|| +| ++||| ||+ |||+| | Sbjct 217 PDALPEVQ-----DELD#AGNKATLPAEADFLLAYSTVPGYYSWRNPGRG 260 |
| Schistosoma japonicum | Query 182 ISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 + || +|| ||||| ||+++||+ || Sbjct 183 VHKLPVEADILVSYSTVPGYIAWRNMTSG 211 |
| Anopheles gambiae str. PEST | Query 167 TPFQEGLR----TFDQLD#AISS-------LPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 | | +|++ | +|#|+|| +|| +|+ | || | | |||+| | Sbjct 129 TKFDKGVKLTKIATDTVD#ALSSSSQRTCVIPTMADVLVMYSAFDGHYSWRNPTHG 183 |
| Aedes aegypti | Query 178 QLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 | # + |+| +|+ | |||+ |+ |||+|+ | Sbjct 184 QEQ#VLYSIPAMADLLVMYSTYDGYYSWRNPRQG 216 |
| Strongylocentrotus purpuratus | Query 183 SSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 | +|+ ||+ ++|+| |||||||+ + | Sbjct 191 SKVPSQSDMLLAYATVPGFVSWRNSERG 218 |
| Xenopus tropicalis | Query 163 EPDATPFQEGLRTFDQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 | || | + | | +# +| +| +||| ||+ |||+| | Sbjct 206 ETDAGPSNDSLET--DAN#PRHKIPVEADFLYAYSTVPGYYSWRNPGRG 251 |
| Contains: Caspase-3 p17 subunit; Caspase-3 p12 subunit | Query 185 LPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 +| +| +||| ||+ |||+|| | Sbjct 187 IPVEADFLYAYSTAPGYYSWRNPKDG 212 |
| Bos taurus | Query 185 LPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 +| +| +||| ||+ |||+| || Sbjct 240 IPVEADFLFAYSTVPGYYSWRNPGSG 265 |
| Geodia cydonium | Query 184 SLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 +||| +| ++|+| ||+||||+ + | Sbjct 221 ALPTEADFVLAYATVPGYVSWRNSEYG 247 |
| Equus caballus | Query 167 TPFQEGLRTFDQLD---#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 | |+ | ++ #| +| +| +||| ||+ |||+ | | Sbjct 63 TELDSGIETDSGIEDDM#ACQKIPVEADFLYAYSTAPGYYSWRNSKDG 109 |
| Gobius niger | Query 167 TPFQEGLRTFDQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 | |+ | |# + +| +| +||| ||+ |||+ +| Sbjct 118 TDLDAGIETDSPDD#EGARIPVEADFLYAYSTAPGYYSWRNTMTG 161 |
| Sus scrofa | Query 181 AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 | +| +| +||| ||+ |||+ | | Sbjct 183 ACQKIPVEADFLYAYSTAPGYYSWRNSKDG 212 |
| Cricetulus griseus | Query 181 AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 | +| +| +||| ||+ |||+ | | Sbjct 183 ACHKIPVEADFLYAYSTAPGYYSWRNSKDG 212 |
| Contains: Caspase-7 subunit p20; Caspase-7 subunit p11 | Query 185 LPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 +| +| +||| ||+ |||+| | Sbjct 213 IPVEADFLFAYSTVPGYYSWRNPGKG 238 |
| Salmo salar | Query 185 LPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 +| +| +||| ||+ |||+| | Sbjct 155 IPVEADFLFAYSTVPGYYSWRNPGRG 180 |
| Ovis aries | Query 181 AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 | +| +| +||| ||+ |||+ | | Sbjct 152 ACQKIPVEADFLYAYSTAPGYFSWRNSKYG 181 |
| Drosophila melanogaster | Query 185 LPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 +| +| ++||| ||| |||+ | Sbjct 239 IPVHADFLIAYSTVPGFYSWRNTTRG 264 |
| Drosophila pseudoobscura | Query 185 LPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 +| +| ++||| ||| |||+ | Sbjct 236 IPVHADFLIAYSTVPGFYSWRNTTRG 261 |
| Apis mellifera | Query 170 QEGLRTFDQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 +| | | #+ +|+ +| ++||| ||+ |||+ | Sbjct 186 KERTETDGQPA#STFRIPSHADFLIAYSTIPGYYSWRNTTRG 226 |
| Chrysiptera parasema | Query 167 TPFQEGLRTFDQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 | |+ | | +# + +| +| ++|| ||+ |||+ +| Sbjct 111 TDLDAGIET-DSGE#GTTKIPVEADFLYAFSTAPGYYSWRNTMTG 153 |
| Oryzias latipes | Query 169 FQEGLRTFDQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 | ||+ + |# +| +| +||| |+ ||| +| Sbjct 181 FDEGIEHDAKDD#TSEKIPLEADFLFAYSTVSGYYSWRSTANG 222 |
| Aspergillus clavatus NRRL 1 | Query 152 SPEDESPGSNPEPDATPFQEGLRTFDQLD#AISSLPTPSDIFVSYS 196 +|+|+|| | ||||+ + | + # + |+| |+|| | | Sbjct 108 APQDQSPHSEYEPDASTPGSRRQAFGRFR#GVLSIPERSNIFGSGS 152 |
| Takifugu rubripes | Query 172 GLRTFDQLD#AISS-LPTPSDIFVSYSTFPGFVSWRDPKSG 210 |+ | |#+ ++ +| +| ++|| ||+ |||+ || Sbjct 177 GIETDSAAD#SSTTKIPVEADFLYAFSTAPGYYSWRNTTSG 216 |
[Site 2] LTPVVLRPEI115-RKPEVLRPET
Ile115  Arg
Arg
 |
|||||||||
| P10 | P9 | P8 | P7 | P6 | P5 | P4 | P3 | P2 | P1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leu106 | Thr107 | Pro108 | Val109 | Val110 | Leu111 | Arg112 | Pro113 | Glu114 | Ile115 |
 |
|||||||||
| P1' | P2' | P3' | P4' | P5' | P6' | P7' | P8' | P9' | P10' |
| Arg116 | Lys117 | Pro118 | Glu119 | Val120 | Leu121 | Arg122 | Pro123 | Glu124 | Thr125 |
 Sequence conservation (by blast)
Sequence conservation (by blast) Sequence conservation (by blast)
Sequence conservation (by blast)
| Reference peptide (cleaved bond±30 residues) |
|---|
| ASFLRTNRQAAKLSKPTLENLTPVVLRPEIRKPEVLRPETPRPVDIGSGGFGDVEQKDHG |
Summary
| # | organism | max score | hits | top seq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Homo sapiens | 124.00 | 10 | caspase-9S precursor |
| 2 | Pan troglodytes | 110.00 | 4 | PREDICTED: caspase 9 isoform 2 |
| 3 | synthetic construct | 110.00 | 1 | Homo sapiens caspase 9, apoptosis-related cysteine |
| 4 | N/A | 108.00 | 1 | G |
| 5 | Macaca fascicularis | 105.00 | 2 | caspase 9 |
| 6 | Macaca mulatta | 105.00 | 1 | PREDICTED: similar to caspase 9 isoform alpha prep |
| 7 | Mus musculus | 59.30 | 8 | caspase 9 |
| 8 | Rattus norvegicus | 53.90 | 5 | 25 kDa caspase-9 dominant negative protein |
| 9 | Canis familiaris | 48.90 | 2 | PREDICTED: caspase 9, apoptosis-related cysteine p |
| 10 | Canis lupus familiaris | 45.80 | 1 | caspase 9 |
| 11 | Monodelphis domestica | 37.70 | 1 | PREDICTED: similar to ICE-LAP6 |
| 12 | Chromobacterium violaceum ATCC 12472 | 37.70 | 1 | hypothetical protein CV2832 |
| 13 | Bacillus weihenstephanensis KBAB4 | 33.50 | 1 | Extensin-like protein:NEAr transporter |
Top-ranked sequences
| organism | matching |
|---|---|
| Homo sapiens | Query 86 ASFLRTNRQAAKLSKPTLENLTPVVLRPEI#RKPEVLRPETPRPVDIGSGGFGDVEQKDHG 145 ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||#|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||| Query 86 ASFLRTNRQAAKLSKPTLENLTPVVLRPEI#RKPEVLRPETPRPVDIGSGGFGDVEQKDHG 145 |
| Pan troglodytes | Query 86 ASFLRTNRQAAKLSKPTLENLTPVVLRPEI#RKPEVLRPETPRPVDIGSGGFGDV 139 ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||#|||||||||||||||||||||||| Query 86 ASFLRTNRQAAKLSKPTLENLTPVVLRPEI#RKPEVLRPETPRPVDIGSGGFGDV 139 |
| synthetic construct | Query 86 ASFLRTNRQAAKLSKPTLENLTPVVLRPEI#RKPEVLRPETPRPVDIGSGGFGDV 139 ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||#|||||||||||||||||||||||| Query 86 ASFLRTNRQAAKLSKPTLENLTPVVLRPEI#RKPEVLRPETPRPVDIGSGGFGDV 139 |
| N/A | Query 86 ASFLRTNRQAAKLSKPTLENLTPVVLRPEI#RKPEVLRPETPRPVDIGSGGFGDV 139 |||||||||| |||||||||||||||||||#|||||||||||||||||||||||| Sbjct 86 ASFLRTNRQAGKLSKPTLENLTPVVLRPEI#RKPEVLRPETPRPVDIGSGGFGDV 139 |
| Macaca fascicularis | Query 86 ASFLRTNRQAAKLSKPTLENLTPVVLRPEI#RKPEVLRPETPRPVDIGSGGFGDV 139 |||||||||| |||||||||||||||||||#|||||||||||||||||||| ||| Sbjct 72 ASFLRTNRQAVKLSKPTLENLTPVVLRPEI#RKPEVLRPETPRPVDIGSGGCGDV 125 |
| Macaca mulatta | Query 86 ASFLRTNRQAAKLSKPTLENLTPVVLRPEI#RKPEVLRPETPRPVDIGSGGFGDV 139 |||||||||| |||||||||||||||||||#|||||||||||||||||||| ||| Sbjct 86 ASFLRTNRQAVKLSKPTLENLTPVVLRPEI#RKPEVLRPETPRPVDIGSGGCGDV 139 |
| Mus musculus | Query 99 SKPTLENLTPVVLRPEI#R-----KPEVLRPETPRPVDIGSGGFGDV 139 |+| + ||||||| || # ||||||||||||||||||| || Sbjct 131 SQPAVGNLTPVVLGPEE#LWPARLKPEVLRPETPRPVDIGSGGAHDV 176 |
| Rattus norvegicus | Query 99 SKPTLENLTPVVLRPEI#R-----KPEVLRPETPRPVDIGSGGFGDV 139 |+| | ||||||| || # +|||| |||||||||||| || Sbjct 132 SQPALGNLTPVVLGPEE#LWPTRLRPEVLTPETPRPVDIGSGRAHDV 177 |
| Canis familiaris | Query 86 ASFLRTNRQAAKLSKPTLENLTPVVLRPEI#RKPEVLRPETPRPVDIGSGGFGDV 139 || | +||| || | | |||| | # +|+|+|| ||| | ||| | || Sbjct 86 ASCLTMSRQADP-SKLTPGKLAPVVLGPAE#LQPQVVRPSVPRPTDNGSGRFSDV 138 |
| Canis lupus familiaris | Query 99 SKPTLENLTPVVLRPEI#RKPEVLRPETPRPVDIGSGGFGDV 139 || | | |||| | # +|+|+|| ||| | ||| | || Sbjct 129 SKLTPGKLAPVVLGPAE#LQPQVVRPSVPRPTDNGSGRFSDV 169 |
| Monodelphis domestica | Query 86 ASFLRTNRQAAKLSKPTLENLTPVVLRPEI#RKPEVLRPETPRPVDIGSGG 135 |+ | ||+| | +| | || | | || # +| +|+ | | | || Sbjct 84 AALLSENREAGKCLRPHL-NLGPPVSRPLC#DPEQVTKPQLPSPYHSGGGG 132 |
| Chromobacterium violaceum ATCC 12472 | Query 96 AKLSKPTLENLTPVVLRPEI#RKPEVL-RPETPRPVDIGSGGFGDVEQ 141 | |||| |+|+ + ||| #+ |+| | |+| + | || + | Sbjct 111 AALSKPQLQNVFMAIERPET#KPGEILPGEEVPQPTPVNPGEFGSIGQ 157 |
| Bacillus weihenstephanensis KBAB4 | Query 92 NRQAAKLSKPTLENLTPVVLRPEI#RKPEVLRPETPRP 128 | + ++ || +| | | +||+# |||| +|| +| Sbjct 457 NEEKPEVEKPEVEK--PEVEKPEV#EKPEVEKPEVEKP 491 |
* References
[PubMed ID: 19269008] Kim YR, Kim KM, Yoo NJ, Lee SH, Mutational analysis of CASP1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, and 14 genes in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Hum Pathol. 2009 Jun;40(6):868-71. Epub 2009 Mar 9.
[PubMed ID: 19359048] ... Andreoli V, Trecroci F, La Russa A, Valentino P, Condino F, Latorre V, Nistico R, Pirritano D, Del Giudice F, Canino M, Cittadella R, Quattrone A, CASP-9: A susceptibility locus for multiple sclerosis in Italy. J Neuroimmunol. 2009 May 29;210(1-2):100-3. Epub 2009 Apr 8.
[PubMed ID: 19414860] ... Lan Q, Morton LM, Armstrong B, Hartge P, Menashe I, Zheng T, Purdue MP, Cerhan JR, Zhang Y, Grulich A, Cozen W, Yeager M, Holford TR, Vajdic CM, Davis S, Leaderer B, Kricker A, Schenk M, Zahm SH, Chatterjee N, Chanock SJ, Rothman N, Wang SS, Genetic variation in caspase genes and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a pooled analysis of three population-based case-control studies. Blood. 2009 May 4.
[PubMed ID: 19412632] ... Gangwar R, Mandhani A, Mittal RD, Caspase 9 and caspase 8 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to bladder cancer in north Indian population. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009 Jul;16(7):2028-34. Epub 2009 May 2.
[PubMed ID: 19238172] ... Zuo Y, Xiang B, Yang J, Sun X, Wang Y, Cang H, Yi J, Oxidative modification of caspase-9 facilitates its activation via disulfide-mediated interaction with Apaf-1. Cell Res. 2009 Apr;19(4):449-57.
[PubMed ID: 12792650] ... Allan LA, Morrice N, Brady S, Magee G, Pathak S, Clarke PR, Inhibition of caspase-9 through phosphorylation at Thr 125 by ERK MAPK. Nat Cell Biol. 2003 Jul;5(7):647-54.
[PubMed ID: 9651578] ... Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Alnemri ES, Autoactivation of procaspase-9 by Apaf-1-mediated oligomerization. Mol Cell. 1998 Jun;1(7):949-57.
[PubMed ID: 9337844] ... Cohen GM, Caspases: the executioners of apoptosis. Biochem J. 1997 Aug 15;326 ( Pt 1):1-16.
[PubMed ID: 8962078] ... Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Litwack G, Alnemri ES, Molecular ordering of the Fas-apoptotic pathway: the Fas/APO-1 protease Mch5 is a CrmA-inhibitable protease that activates multiple Ced-3/ICE-like cysteine proteases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Dec 10;93(25):14486-91.
[PubMed ID: 8900201] ... Srinivasula SM, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Zangrilli J, Robertson N, Armstrong RC, Wang L, Trapani JA, Tomaselli KJ, Litwack G, Alnemri ES, The Ced-3/interleukin 1beta converting enzyme-like homolog Mch6 and the lamin-cleaving enzyme Mch2alpha are substrates for the apoptotic mediator CPP32. J Biol Chem. 1996 Oct 25;271(43):27099-106.
[PubMed ID: 8900201] ... Srinivasula SM, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Zangrilli J, Robertson N, Armstrong RC, Wang L, Trapani JA, Tomaselli KJ, Litwack G, Alnemri ES, The Ced-3/interleukin 1beta converting enzyme-like homolog Mch6 and the lamin-cleaving enzyme Mch2alpha are substrates for the apoptotic mediator CPP32. J Biol Chem. 1996 Oct 25;271(43):27099-106.
[PubMed ID: 8663294] ... Duan H, Orth K, Chinnaiyan AM, Poirier GG, Froelich CJ, He WW, Dixit VM, ICE-LAP6, a novel member of the ICE/Ced-3 gene family, is activated by the cytotoxic T cell protease granzyme B. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jul 12;271(28):16720-4.
[PubMed ID: 7983002] ... Fernandes-Alnemri T, Litwack G, Alnemri ES, CPP32, a novel human apoptotic protein with homology to Caenorhabditis elegans cell death protein Ced-3 and mammalian interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 9;269(49):30761-4.
[PubMed ID: 1067155] ... Kopp S, Reproducibility of response to a questionnaire on symptoms of masticatory dysfunction. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 1976 Sep;4(5):205-9.
[PubMed ID: 1067155] ... Kopp S, Reproducibility of response to a questionnaire on symptoms of masticatory dysfunction. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 1976 Sep;4(5):205-9.