CL0904 : calpain 6
[ CaMP Format ]
* Basic Information
| Organism | Homo sapiens (human) |
| Protein Names | calpain-like protease; calpamodulin; calpain 6 [Homo sapiens]; Calpain-6; Calpamodulin; CalpM; Calpain-like protease X-linked |
| Gene Names | CAPN6; CALPM, CANPX; CALPM; CANPX; calpain 6 |
| Gene Locus | Xq23; chromosome X |
| GO Function | Not available |
* Information From OMIM
Text: Calpains are calcium-dependent cysteine proteases involved in signal transduction in a variety of cellular processes. A functional calpain protein consists of an invariant small subunit (OMIM:114170) and 1 of a family of large subunits. Dear et al. (1997) used degenerate PCR on mouse genomic DNA to isolate fragments of 2 novel calpains, CAPN5 (OMIM:602537) and CAPN6. The authors assembled a partial cDNA sequence of CAPN6 from several clones in an EST database. Dear et al. (1997) noted that CAPN5 and CAPN6 differ from previously identified vertebrate calpains in that they lack a calmodulin-like domain IV. CAPN6 may be an atypical calpain because it contains only 1 of the 3 conserved cysteine protease active site residues. By RNA dot blot and Northern blot analyses, Dear et al. (1997) found that CAPN6 is expressed as a 4.0-kb transcript predominantly in placenta.
* Structure Information
1. Primary Information
Length: 641 aa
Average Mass: 74.576 kDa
Monoisotopic Mass: 74.529 kDa
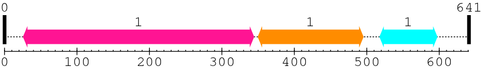
2. Domain Information
Annotated Domains: interpro / pfam / smart / prosite
Computationally Assigned Domains (Pfam+HMMER):
| domain name | begin | end | score | e-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peptidase_C2 1. | 26 | 344 | 283.3 | 5.6e-82 |
| Calpain_III 1. | 350 | 495 | 274.2 | 2.9e-79 |
| C2 1. | 518 | 597 | 55.0 | 2.8e-13 |
3. Sequence Information
Fasta Sequence: CL0904.fasta
Amino Acid Sequence and Secondary Structures (PsiPred):
4. 3D Information
Not Available.
* References
[PubMed ID: 18657900] Rho SB, Byun HJ, Park SY, Chun T, Calpain 6 supports tumorigenesis by inhibiting apoptosis and facilitating angiogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2008 Nov 28;271(2):306-13. Epub 2008 Jul 26.